The mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) test is a type of DNA test available to genealogists in addition to autosomal and Y-DNA tests[1], MyHeritage provides autosomal DNA testing to customers.
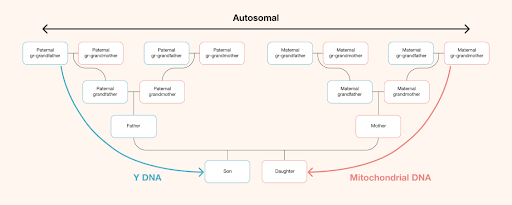
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited by both males and females from their mother. Women pass their mitochondrial DNA to both sexes of their children, with no admixed DNA from the fathers. Males inherit their mitochondrial DNA from their mother, but do not pass it to their children. Everyone inherits their mother’s mitochondrial DNA - who inherits it from her mother, and so forth on up the mother-to-mother matrilineal line of all women.
Research your ancestors on MyHeritage
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited by both males and females from their mother. Women pass their mitochondrial DNA to both sexes of their children, with no admixed DNA from the fathers. Males inherit their mitochondrial DNA from their mother, but do not pass it to their children. Everyone inherits their mother’s mitochondrial DNA - who inherits it from her mother, and so forth on up the mother-to-mother matrilineal line of all women.
Mitochondrial DNA is a powerful genealogy tool, providing a separate type of matching for the direct matrilineal line, along with identifying the geographical source of their direct maternal ancestor. [2]
FamilyTreeDNA tests mitochondrial DNA specifically for genealogy and includes several important tools.
- Matching with other mitochondrial testers
- Earliest known ancestors for your matches
- Trees of your matches
- Haplogroup determination and assignment
- Migration journey for your haplogroup
- Ancestral origins – where your matches’ ancestors are found around the world
- Haplogroup origins – where the haplogroups of your matches are found around the world
- Group projects that you can join[3]
- Free public Mitochondrial HaploTree, with countries[4]
The Power of Mitochondrial DNA
In most western cultures, females change their surname when they marry, often resulting in difficulty identifying their parents. Mitochondrial DNA follows the direct mother-to-mother maternal path, which, combined with family trees provides laser-focused genealogical information for that specific line – and only that line.
Mitochondrial DNA has the ability to break through maternal-line brick walls.
Haplogroups Are Genetic Clans
Haplogroups are genetic clans. Different haplogroups are found in different parts of the world and in different populations. For example, haplogroups for European, Asian, African, Native American and Jewish populations have evolved uniquely over time.
Today, we can identify broad groups through haplogroup identification.[5]
Matching to other testers occurs with mitochondrial DNA testing at FamilyTreeDNA. By viewing haplogroups only, you can eliminate potential lineages, but you cannot confirm a specific lineage without traditional genealogical research combined with autosomal DNA.
Matches
As with autosomal DNA, mitochondrial DNA matches are critical first steps in identifying a common ancestor. Gathering and collecting the haplogroup of each ancestral line is a good way to learn more about every ancestor in your tree.[6]
Autosomal DNA matching along with mitochondrial results complement each other well.
When ordering a mitochondrial DNA test, be sure to order or upload an autosomal test for each tester too.
See also
Explore more about ethnicity estimates
- MyHeritage DNA at MyHeritage
- Ethnicities around the world at MyHeritage
- What Is My Ethnicity? How MyHeritage Estimates Ethnicities at MyHeritage Knowledge Base
- Where's My Ethnicity?!: Why An Ethnicity Might Not Show Up In Your DNA (and How To Find Evidence Of It Anyway) at MyHeritage Knowledge Base
- Foundations in DNA 4 of 5: Mitochondrial DNA at Legacy Family Tree Webinars
- 10 Ways to Find Your Native American Ancestor Using Y, Mitochondrial and Autosomal DNA at Legacy Family Tree Webinars
- Wringing Every Drop out of Mitochondrial DNA at Legacy Family Tree Webinars
- Using Mitochondrial DNA Testing for Genealogical Problem Solving at Legacy Family Tree Webinars
References
- ↑ https://dna-explained.com/2012/10/01/4-kinds-of-dna-for-genetic-genealogy/
- ↑ https://www.familytreedna.com/public/mt-dna-haplotree/L
- ↑ https://www.familytreedna.com/group-project
- ↑ https://www.familytreedna.com/public/mt-dna-haplotree/L
- ↑ https://dna-explained.com/2021/02/03/haplogroup-matching-what-it-does-and-doesnt-mean/
- ↑ https://dna-explained.com/mitochondrial-dna/


